Now that we have learned about different sources of energy, we might ask which of them is the best? Which is the most environmentally friendly and which the least harmful for the climate? And which is the cheapest?
The answers to these questions are not as simple as might seem at first glance. We must consider a lot of factors when we compare different fuels.
- Greenhouse gas emissions in their production and
- Emissions (during production and use) of harmful substances that are hazardous to human health and the environment.
- The cost of transporting fuel from the place it is produced to an electricity generating plant.
- The cost of distributing heat and electricity to consumers at a distance from where the heat and electricity is generated.
- The cost of building and operating a power plant and dismantling it at the end of its service life.
- Environmental and human costs (dealing with accidents, treating victims, compensating their families, and planting trees to offset greenhouse gas emissions).
- The climatic and geographical location of electricity generating What source will they use for their water needs and how will the water be cleaned? What are the prevalent winds at the location and are there any critical weather or seismic conditions? Are there convenient transportation routes for the supply of raw materials? What natural habitats and landscapes and human settlements are in the vicinity?
It makes no sense to discuss the efficiency of technology and the cost of energy in isolation from issues of climate change, the environment and health. So, before deciding what kind of power stations need to be built and operated, a wide variety of assessments (technical, economic, environmental, etc.) must be carried out.
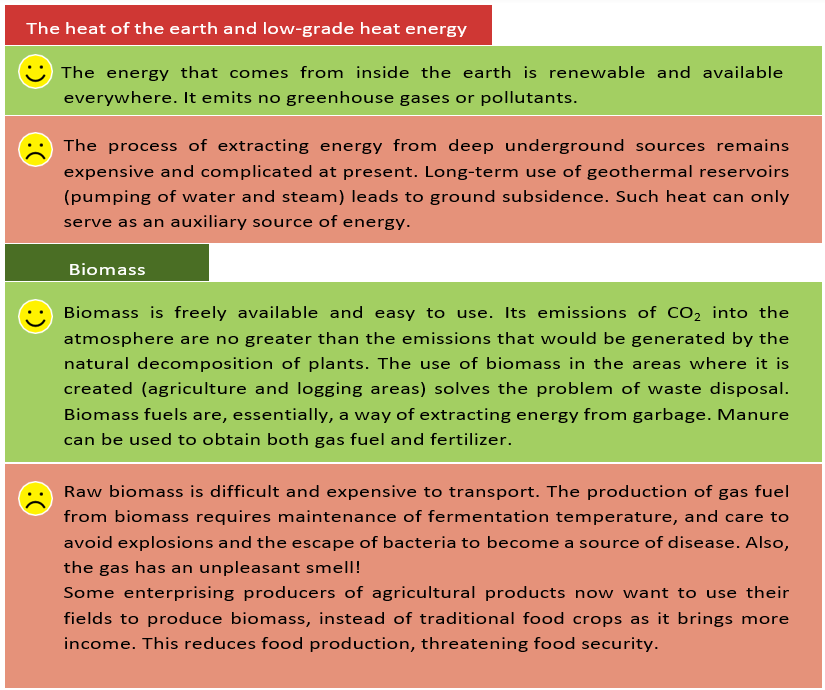
Let’s recall and compare the advantages and disadvantages of the main natural sources of energy once again.







If renewable energy is inexhaustible and environmentally friendly, why not change over completely from coal, oil, gas, and nuclear power to green technologies?
The fact is that there are still limitations to the mass development of renewable energy. The operation of power plants using renewable energy sources depends on climate conditions, which is why they are called variable sources of energy (wind strength, the presence of rivers, the number of sunny days). Renewable energy-generating plants usually have their own site-specific design. So, the successful use of renewable sources requires a high investment of effort and money at the time of their design and construction. When the capacity of renewable generation plants reaches a certain level, further expansion requires large investment in the electricity network and gradual transition to the so-called ‘smart grids’. Nevertheless, new technologies are steadily making energy production from renewable sources more efficient and driving down the production cost and expanding the market.
Energy is always in demand, so the energy industry, particularly the production and trade in oil, gas, and coal, is very profitable. The huge amounts of money in this industry result in frequent and serious disagreements between government, business, and environmental civil society organizations. This is a global problem. But in the long term, people are moving towards an understanding of the urgent changes needed for the future of humanity and of the planet. The introduction of new, climate-friendly technologies is delayed by the inertia of human thinking. Our planet and the universe are ready to give us their energy, but in return we must learn to use our natural resources in a way that helps the climate and does not destroy it for the sake of short-term benefits.
QUESTIONS
1
What sources of energy were used in ancient times?
2
What ways do you know of using solar panels?
3
List all the factors that must be taken into account if we are to determine the total cost of generating electricity from one or other source of energy.
4
Electric engines do not produce harmful emissions. So can we consider them to be the most environmentally friendly type of engine?
5
Flat solar cells are installed on the roofs of houses at an angle to the horizon equal to the latitude of the place where they are installed. Why do you think that is?
6
What are the main barriers to the fast growth of renewable energy capacity?

TASKS

1
2
Divide into groups by different ways of producing electricity.
Each group should prepare a report to defend its way of producing energy, including information about problems associated with all the other ways. Then prepare and hold a discussion about the benefits and harm caused by different types of power-generating plants, making it relevant to the area where you live.


